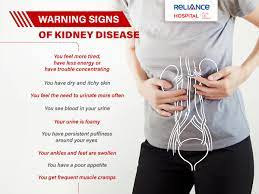
Kidney problems can range from mild to severe, so it's important to be aware of potential warning signs. Keep in mind that these symptoms can also be indicative of other health issues, so it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some common warning signs of kidney problems:
Changes in Urination:
Increased frequency of urination, especially at night.
Difficulty in urinating or a feeling of incomplete emptying.
Decreased urine output.
Foamy or bubbly urine.
Blood in Urine (Hematuria):
This can be visible to the naked eye or detected only under a microscope.
Swelling (Edema):
Especially in the legs, ankles, feet, and around the eyes.
Fatigue and Weakness:
Generalized tiredness, lack of energy.
Persistent Back Pain:
Pain in the middle or lower back, typically on one side.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension):
Kidneys play a key role in regulating blood pressure. Chronic kidney disease can lead to hypertension, and hypertension can also cause kidney damage.
Changes in Skin Tone:
Skin may appear darker or lighter.
Itching and Dry Skin:
Due to a buildup of waste products in the body.
Nausea and Vomiting:
Especially in the morning or after a meal.
Loss of Appetite:
Often accompanies nausea and vomiting.
Metallic Taste in Mouth or Ammonia Breath:
Due to a buildup of waste products.
Shortness of Breath:
Can be a sign of fluid buildup in the lungs.
Muscle Cramps and Weakness:
Especially in the legs.
Dizziness and Trouble Concentrating:
Due to anemia and waste buildup in the body.
Puffiness Around the Eyes:
Swelling in the delicate tissues around the eyes.
Frequent Headaches:
Often due to high blood pressure.
Easy Bruising and Bleeding:
Because of decreased production of blood-clotting proteins.
Frequent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
Kidney problems can make you more susceptible to UTIs.
Cardamom is a spice that has been used for centuries for its culinary and medicinal properties. While there is limited scientific research specifically on the health benefits of cardamom water on an empty stomach, there are some potential advantages associated with consuming cardamom in various forms, including as a spice in water. Here are some potential health benefits: Digestive Health: Cardamom is known for its carminative properties, which means it can help in relieving gas and bloating. Drinking cardamom water on an empty stomach may stimulate digestion and reduce symptoms of indigestion. Detoxification: Some people believe that cardamom water may help flush out toxins from the body. The antioxidants present in cardamom may contribute to detoxification processes. Metabolism Boost: There is some evidence to suggest that cardamom may have a positive impact on metabolism. A faster metabolism can potentially aid in weight management. Anti-inflammatory Properties: Cardamom conta...
Comments
Post a Comment