Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii. Despite its name, Rocky Mountain spotted fever is not limited to the Rocky Mountain region and can occur in various parts of North, Central, and South America.
The bacterium is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, especially the American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis), Rocky Mountain wood tick (Dermacentor andersoni), and brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus). These ticks become infected when they feed on small mammals, such as rodents or dogs, that carry the bacteria.
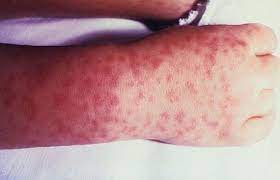
Symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever typically appear within 2 to 14 days after a tick bite and may include:
High fever
Severe headache
Muscle aches
Chills
Fatigue
Nausea and vomiting
Rash (may start on the wrists and ankles and spread to other parts of the body)
If left untreated, Rocky Mountain spotted fever can be a serious and potentially fatal illness. It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you have been bitten by an infected tick and are experiencing symptoms.
Diagnosis is usually based on clinical symptoms, the patient's history of tick exposure, and laboratory tests. Treatment typically involves the use of antibiotics, such as doxycycline, which is effective against the bacteria causing the infection. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for a positive outcome.
Preventive measures include avoiding tick-infested areas, using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, checking for ticks after outdoor activities, and promptly removing ticks if found. If you suspect you've been bitten by a tick and develop symptoms, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Cardamom is a spice that has been used for centuries for its culinary and medicinal properties. While there is limited scientific research specifically on the health benefits of cardamom water on an empty stomach, there are some potential advantages associated with consuming cardamom in various forms, including as a spice in water. Here are some potential health benefits: Digestive Health: Cardamom is known for its carminative properties, which means it can help in relieving gas and bloating. Drinking cardamom water on an empty stomach may stimulate digestion and reduce symptoms of indigestion. Detoxification: Some people believe that cardamom water may help flush out toxins from the body. The antioxidants present in cardamom may contribute to detoxification processes. Metabolism Boost: There is some evidence to suggest that cardamom may have a positive impact on metabolism. A faster metabolism can potentially aid in weight management. Anti-inflammatory Properties: Cardamom conta...
Comments
Post a Comment